Unlocking the Gut-Brain Connection: Understanding Its Mechanisms
Mar 06, 2024 By Madison Evans
Have you felt butterflies in your stomach when you are nervous? Do you notice that you feel bloated and your mood changes after eating some foods? There appears to be a strong correlation between gut and brain functions. The link which is called gut-brain connection is like an underground passage that allows your stomach and your brain to talk to each other. In short, it translates that what happens in your stomach could determine your emotional and mental health. In this article, we will take a closer view of this amazing link between your gut and your brain, looking at how they talk and on the influence of this on your overall health.
What is brain gut connection?
The gut-brain link strongly connects our digestion system (the gut) and the brain. It is like a super highway in communications, with messages going back and forth between the two.
Our gut conveys signals to the brain when we eat. This makes the brain aware of what is going on in the body. Similarly, the brain can send signals that change their function to our guts. This bond dramatically influences our health and well-being, regulating many aspects, from digestion to mood regulation. Understanding and encouraging this relationship is vital to having an excellent physical and psychological state.
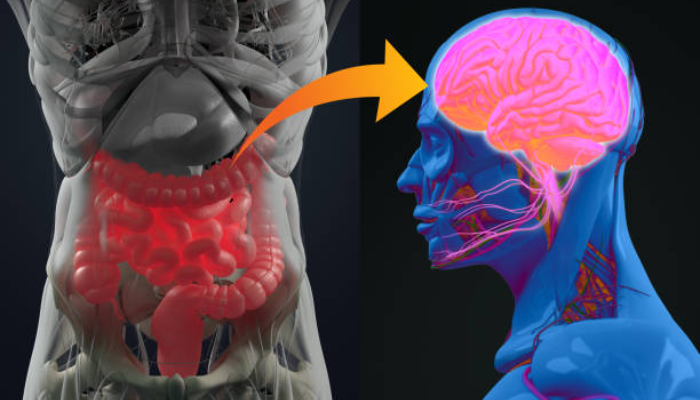
How it work?
The gut-brain linkage is like a unique line of communication between our brain and stomach. It's like they're best friends because they talk so much. This nerve system is made of nerves, hormones, and other messengers that send messages both ways. When we eat something, our stomach conveys it to our brain about what's happening. And sometimes, the brain argues with us, and then our stomach feels different. The back-and-forth of this chat matters as it impacts how we feel internally and externally.
The most crucial thing in this concern is the vagus nerve. It's like a ring from our brain to our stomach. The brain can utilize this phone line to communicate the nerve feelings to our stomach, resulting in anxiety or nausea. And when our gut is not in good shape, it can call our brain, bringing us bad moods or tiredness.
How to support it?
Eat a Balanced Diet
Eating a well-balanced diet is the most efficient method to support a good connection between your gut and brain. A balanced diet by eating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins ensures that essential nutrients help gut health and brain function. Besides being high in fibre, foods like fruits, vegetables, and legumes can be helpful for "good bacteria" growth in the intestines, promo, and promote health. Also, getting omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, plants like flaxseeds, and walnuts will help fight inflammation in the gut and brain, building a strong link between the two.
Manage Stress
Stress can destroy the relationship between the gut and the brain, thus causing many digestive issues and disrupting mood. Discovering healthy methods to manage stress is one of the critical strategies for maximum communication between the gut and the brain. Practices like mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and being in nature are associated with decreased stress levels and better general well-being. "Putting self-care first" and sticking to activities that lead to healing of both gut health and mental health can have a strong positive effect on both.
Prioritize Sleep
Gut-brain connection is maintained through quality sleep. Lack of sleep may results in microbial imbalance and body inflammation causing damage both on gut and brain function. Try to get about 7-9 hours of sleep a day and communicate well between the gut and the brain. Establishing a regular sleep pattern, bedtime routine and a sleeping environment that is comfortable may result in high quality sleep as well as well-being in general.
Hydration
A well hydrated stomach means a good connection with your mind; water keeps things running efficiently within our digestive tract so that all nutrients can be properly absorbed while waste gets excreted. Dehydration can result in constipation and bloating, among other digestive problems, which, in turn, can affect our mood and cognitive functioning negatively. The goal is to drink a lot of water daily to maintain communication between your gut and the brain.
Connect with Others
Social ties have an inherent value in promoting excellent gut-brain health. Elapsed time with peers and family members can lessen the effects of loneliness and isolation that are linked to poor gut health and mental state. Participate in exciting activities that help you interact with others, such as clubs or voluntary services, or chat with friends. Cultivating solid interpersonal ties will strengthen the relationship between your gut and brain and maintain overall health and happiness.

Limit Alcohol and Caffeine
Excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeine can ruin the gut-brain connection and result in digestive problems and mood issues. Although moderate drinking of alcohol and coffee is safe and sometimes even suitable for the majority of people, excessive consumption can have negative impacts on gut health and mental state. Decrease your alcohol and caffeine intake and drink less sugar-portion drinks, e.g., herbal tea or sparkling water.
Enjoy a Lot of Sunshine
Sunlight exposure is significant for physical and mental health. Sunlight works to help the body produce vitamin D, which is important for gut health and mood regulation. Similarly, spending time in fresh air and under sunlight can decrease stress and enhance overall mood. Get 15-30 minutes of sun exposure daily to improve mental health through the gut-brain connection.
Conclusion
The gut-brain connection is vital for our health. The gut and brain are good communicators, influencing how we break down food and how we feel emotionally and mentally. This link will also help us understand that diet and how much stress we have can influence our gut and mood. Proper food and stress reduction methods can maintain a healthy gut. This, in turn, leads to better health of the whole body.







