Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Jun 15, 2024 By Nancy Miller
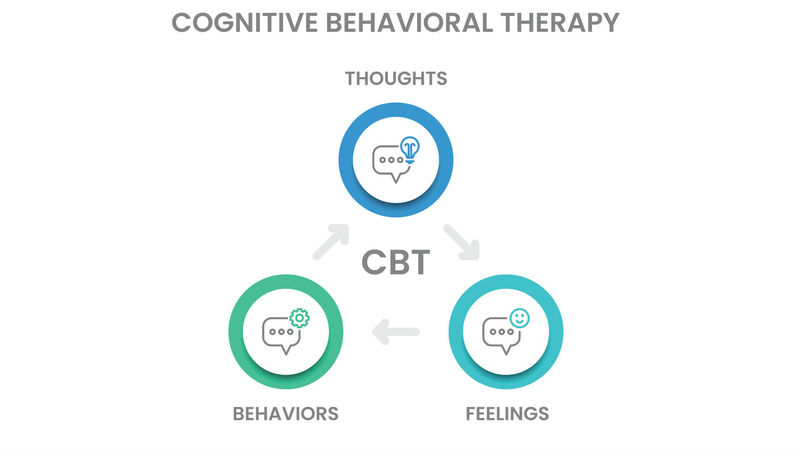
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, also known as CBT, is a popular form of talk therapy that works on finding and changing harmful thought patterns, emotions, and actions. Based on cognitive psychology principles which highlight the link between thoughts feelings and behaviors. This approach aims to encourage adaptive ways of coping while enhancing general well-being. In this article, we are going to discuss about three basic ideas which form the basis for Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. We will also look at how these ideas help in creating positive results for mental health.
1. Identification of Maladaptive Patterns
The initial principle of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is recognizing maladaptive patterns in thinking, feeling, and behaving. In a shared process of exploring and analyzing, people discover distorted thoughts as well as bad self-perceptions which cause emotional problems along with malfunctioning behaviors. Therapists use different methods like thought records, behavioral experiments, and Socratic questioning to help with identifying these wrong patterns. As people become more aware and knowledgeable about these recurring patterns, they are prepared to question and reshape unproductive thinking that leads to transformation.
Besides regular methods of therapy, technological progress has also allowed for the creation of digital instruments that assist in recognizing maladaptive patterns. Mobile apps and online systems provide interactive tasks and self-monitoring capabilities to help people observe their thoughts and actions immediately. They give instant feedback along with graphical illustrations of patterns, which encourages users to actively work towards understanding themselves more effectively as well as developing personally.
- Tech Integration: Utilize mobile apps and online platforms for real-time tracking and feedback on maladaptive patterns.
- Peer Support: Engage in support groups or peer networks to gain insights and perspectives from others facing similar challenges.
2. Behavioral Activation and Experimentation
The next principle of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is about behavioral activation and experimentation for adaptive coping and problem-solving abilities. This method highlights the active involvement of people in significant actions and tests of behavior, designed to check other possible ideas or tactics. Through arranged behavioral treatments, people understand how to interrupt the pattern of evading and retracting that is frequently linked with depression and anxiety. Through slowly bringing back enjoyable and satisfying activities, people can feel that they are in control and successful. This improves their general mood and ability to function.
The strength of mindfulness, when combined with behavioral activation, is its focus on current-moment awareness and acceptance. Mindfulness-based methods teach people to observe their thoughts and feelings without judging them. This can assist individuals in reacting to situations with more clearness and purposefulness. When mindfulness techniques such as deep breathing exercises or body scans are incorporated into everyday habits, it fosters enhanced emotional control and adaptability.
- Mindfulness Integration: Combine behavioral activation with mindfulness techniques to enhance emotional regulation and resilience.
- Environmental Modification: Create supportive environments that facilitate engagement in meaningful activities and promote positive reinforcement.
3. Cognitive Restructuring and Reframing
The third CBT principle includes cognitive restructuring and reframing to question and change irrational or twisted beliefs. This highlights how thinking processes affect emotional understanding as well as behavioral reactions. By using methods like guided imagery, mindfulness-based interventions, or other approaches related to restructuring cognition - people can develop skills in challenging negative interpretations and catastrophic thoughts. By substituting illogical beliefs with better adaptive and balanced viewpoints, people can foster resilience and enhance their ability to cope with difficulties in life.
The merging of good psychology with cognitive restructuring can support a therapy method that is centered on strengths, highlighting the natural resources and capabilities of each person. Positive psychology interventions concentrate on finding and using personal strong points, virtues, and principles to improve psychological healthiness and gratification. When therapists motivate their clients to develop gratefulness, hopefulness, and self-kindness they help create important changes in viewpoint while also promoting feelings of strength and control over life situations.
- Strengths-Based Approach: Incorporate positive psychology interventions to leverage personal strengths and values.
- Holistic Perspective: Consider the broader context of individuals' lives, including social, cultural, and environmental factors, when addressing cognitive restructuring.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy

Even though Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) provides good instruments and skills for helping people with mental health problems, there are some traps that one could fall into. A main pitfall is the inclination to simplify intricate psychological matters. CBT works on the understanding that thoughts, emotions, and actions are linked together but it's important to appreciate how complex human experience can be. Therapists must not simplify clients' concerns into simple formulas or ready-made answers, but rather accept the intricacy and distinctiveness of each person's situation.
Additionally, it's very important not to become too fixed or strict in using CBT. Even though CBT offers a solid structure for therapy, we must keep flexible and open to changes in the requirements and choices of our clients. Therapists should be ready to adjust their methods and steps according to unique variations, cultural elements, and therapeutic bonds.
- Avoid Oversimplification: Resist the temptation to reduce complex psychological issues to simplistic formulas or solutions.
- Maintain Flexibility: Remain open-minded and adaptable to clients' unique needs and preferences, adjusting interventions as necessary for optimal outcomes.
Conclusion
To sum up, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a methodical and proven way to deal with many mental health problems. It concentrates on recognizing patterns that don't work well, activating behavior, trying things out, restructuring thoughts, and thinking differently, all of these help people take charge of their mindsets and actions. When they integrate what they learn into real-life situations, it enables them to accept positive alterations and strengthen their ability to withstand difficulties. For people who are suffering from anxiety, depression, or other mental difficulties, CBT offers a useful structure to encourage personal development and good psychological health.







